electron domain geometry|electron pair geometry vs molecular geometry : Bacolod The geometry of a molecule includes a description of the arrangements of the atoms in the molecule. At a simple level, the molecular structure tell us . Tingnan ang higit pa Caesars Palace Hotel & Casino 3570 Las Vegas Boulevard South, Las Vegas Strip, Las Vegas, NV 89109, United States of America – Excellent location – show map – Train Access
electron domain geometry,In each of the molecules considered up to this point, the electron pairs are either in single bond or in lone pairs. In current form, the Electron Domain model does not account for the observed geometry of C2H 4, in which each H−C−H bond angle is 116.6o and each H−C−C bond angle is 121.7o and . Tingnan ang higit paWe begin by assuming a Lewis structure model for chemical bonding based on valence shell electron pair sharing and the octet rule. We thus assume the . Tingnan ang higit paWe begin by assuming a Lewis structure model for chemical bonding based on valence shell electron pair sharing and the octet rule. We thus assume the . Tingnan ang higit paWe should expect that the properties of molecules, and correspondingly the substances which they comprise, should depend on the details of the . Tingnan ang higit pa
The geometry of a molecule includes a description of the arrangements of the atoms in the molecule. At a simple level, the molecular structure tell us . Tingnan ang higit paLearn how to use electron domains to predict the molecular geometry of a molecule. Electron domains are the number of lone pairs or bond locations around an atom, and .

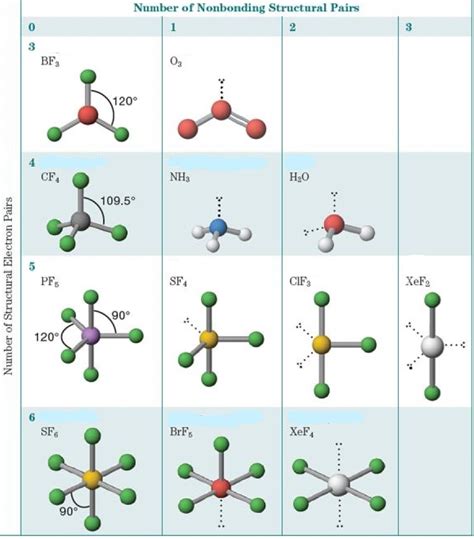
Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) shows the various molecular geometries for the five VESPR electronic geometries with 2 to 6 electron domains. When there .Learning Objectives. To use the VSEPR model to predict molecular geometries. To predict whether a molecule has a dipole moment. The Lewis electron-pair approach can be .electron pair geometry vs molecular geometry The valence shell electron-pair repulsion (VSEPR) model is used to predict the shapes of molecules and polyatomic ions. VSEPR is based on the idea that the “groups” or “clouds” of electrons surrounding an atom will adopt an arrangement that . Professor Davis explains how to identify electron domains and use VSEPR Theory to ultimately predict the molecular geometry of simple compounds, including ex.The VSEPR Theory of Molecular Geometry. Go to an Overview of Three to Six Electron Domains. Back to VSEPR Menu. VSEPR stands for Valence Shell Electron Pair .Explore molecule shapes by building molecules in 3D! How does molecule shape change with different numbers of bonds and electron pairs? Find out by adding single, double or . © 2024 Google LLC. In this lesson, Chad covers VSEPR Theory (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) and Molecular Geometry. He begins by explaining how the different pairs of .

Molecular Geometries. The VSEPR theory describes five main shapes of simple molecules: linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, and octahedral. LEARNING .The term electron geometry is the name of the electron pair/groups/domains on the central atom, whether they are bonding electrons or non-bonding electrons. Electron pairs are electrons that .
Examples: In a water molecule, H 2 O two of the central oxygen atom’s valence electrons form two bond pairs with the hydrogen atoms, while the remaining four electrons form two lone pairs. Therefore, the molecular .We recommend using the latest version of Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or Edge. Explore molecule shapes by building molecules in 3D! How does molecule shape change with different numbers of bonds and electron pairs? Find out by adding single, double or triple bonds and lone pairs to the central atom. Then, compare the model to real molecules! Figure 5.9.5 5.9. 5: (a) The electron-pair geometry for the ammonia molecule is tetrahedral with one lone pair and three single bonds. (b) The trigonal pyramidal molecular structure is determined from the electron-pair geometry. (c) The actual bond angles deviate slightly from the idealized angles because the lone pair takes up a larger .AXE Method. Another way of looking at molecular geometries is through the “AXE method” of electron counting. A in AXE represents the central atom and always has an implied subscript one; X represents the number of sigma bonds between the central and outside atoms (multiple covalent bonds—double, triple, etc.— count as one X); and E represents .The required geometry can again be found by trying to place five points on the surface of a sphere with maximum distances amongst these points. A little experimentation reveals that this can be achieved by placing the five points to form a trigonal bipyramid. Hence, Electron Domain theory accounts for the geometry of PCl5. Second, SF6
Simpler to apply than the original model and supported by the analysis of electron density distributions with the Laplacian operator, the reformulation of the VSEPR model of molecular geometry presented here is based on the concept of electron domains. In this form it is suitable as foundation for a qualitative understanding of the geometry of a .
Count the number of electron domains around the central atom. Determine the electron geometry according to the VSEPR theory. Determine the molecular geometry based on the positions of only the bonded atoms. Common geometries: 2 electron domains: Electron-domain geometry: linear (angle = 180°) 1 Molecular geometry: linear (AX 2) .Each area where electrons exist is called an "electron domain" or simply "domain." It does not matter how many electrons are present, from one to six, it is still just one domain. Now a domain with six electrons in it (a triple bond) is bigger (and more repulsive) than a lone-electron domain. . The VSEPR Model of Molecular Geometry (1991) by .
Electron Domain And Molecular Geometry. In chemistry and physics, the molecular geometry describes the geometric arrangement of the atoms that form a molecule. It is determined by the nature of the chemical bonds between the atoms. These constraints result in the molecule adopting a regular geometric form, like a polyhedron or a sphere. In this lesson, Chad covers VSEPR Theory (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) and Molecular Geometry. He begins by explaining how the different pairs of .2 has 2 electron domains, resulting in a linear electron domain geometry. Both electron domains are bonding pairs, so CO 2 has a linear molecular geometry with a bond angle of 180°. Practice Problems: VSEPR Theory . Predict the electron domain geometry, molecular geometry, and bond angles of the following molecules after drawing valid . 🎯 Want to ace chemistry? Access the best chemistry resource at http://www.conquerchemistry.com/masterclass📗 Need help with chemistry? Download 12 Secrets t. The angles between electron domains are determined primarily by the electronic geometry (e.g., 109.5° for a steric number of 4, which implies that the electronic shape is a tetrahedron) These angles are adjusted by the hierarchy of repulsions: (lone pair - lone pair) > (lone pair - bond) > (bond - bond) . The domain geometry for a molecule with four electron pairs is tetrahedral, as was seen with CH4 CH 4. In the ammonia molecule, one of the electron pairs is a lone pair rather than a bonding pair. The molecular geometry of NH3 NH 3 is called trigonal pyramidal (see figure below). Figure 9.15.3 9.15. 3: Ammonia molecule.2. The carbon atom forms two double bonds. Each double bond is a group, so there are two electron groups around the central atom. Like BeH 2, the arrangement that minimizes repulsions places the groups 180° apart. 3. Once again, both groups around the central atom are bonding pairs (BP), so CO 2 is designated as AX 2.Electron pairs, being negatively charged, repel each other to be as far apart as possible around the central atom. *Lone pairs of electrons reduce bond angles slightly. Provide electron domain and molecular geometries for the following: Chad explains VSEPR Theory, electron domain geometry, and molecular geometry for molecules having 2, .electron domain geometryWe can use the VSEPR model to predict the geometry of most polyatomic molecules and ions by focusing on only the number of electron pairs around the central atom, ignoring all other valence electrons present.According to this model, valence electrons in the Lewis structure form groups, which may consist of a single bond, a double bond, a triple bond, .
electron domain geometry electron pair geometry vs molecular geometryWe can use the VSEPR model to predict the geometry of most polyatomic molecules and ions by focusing on only the number of electron pairs around the central atom, ignoring all other valence electrons present.According to this model, valence electrons in the Lewis structure form groups, which may consist of a single bond, a double bond, a triple bond, .
electron domain geometry|electron pair geometry vs molecular geometry
PH0 · how to find electron domains
PH1 · how to determine electron geometry
PH2 · electron pair geometry vs molecular geometry
PH3 · electron geometry chart
PH4 · electron domain geometry vs molecular shape
PH5 · electron domain geometry table
PH6 · electron domain geometry chart
PH7 · electron domain geometry calculator
PH8 · Iba pa